2025 Discovery of more Saturnian Moons
(For immediate release)
View image here
The International Astronomical Union recognized the discovery of 128 new moons of Saturn by astronomers from Taiwan, Canada, USA, and France on March 11/2025.
The team used the Canada France Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) to repeatedly monitor the sky around Saturn between 2019 to 2021 in minute detail, combining multiple images to strengthen an astronomical object’s signal. This initial run yielded 64 moons – and an even larger number of other objects that, at that time, couldn’t be designated.
“With the knowledge that these were probably moons, and that there were likely even more waiting to be discovered, we revisited the same sky fields for three consecutive months in 2023,” said lead researcher Dr. Edward Ashton, postdoctoral fellow in the Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics at Academia Sinica, who received his Astronomy PhD at the University of British Columba. “Sure enough, we found 128 new moons. Based on our projections, I don’t think Jupiter will ever catch up.”
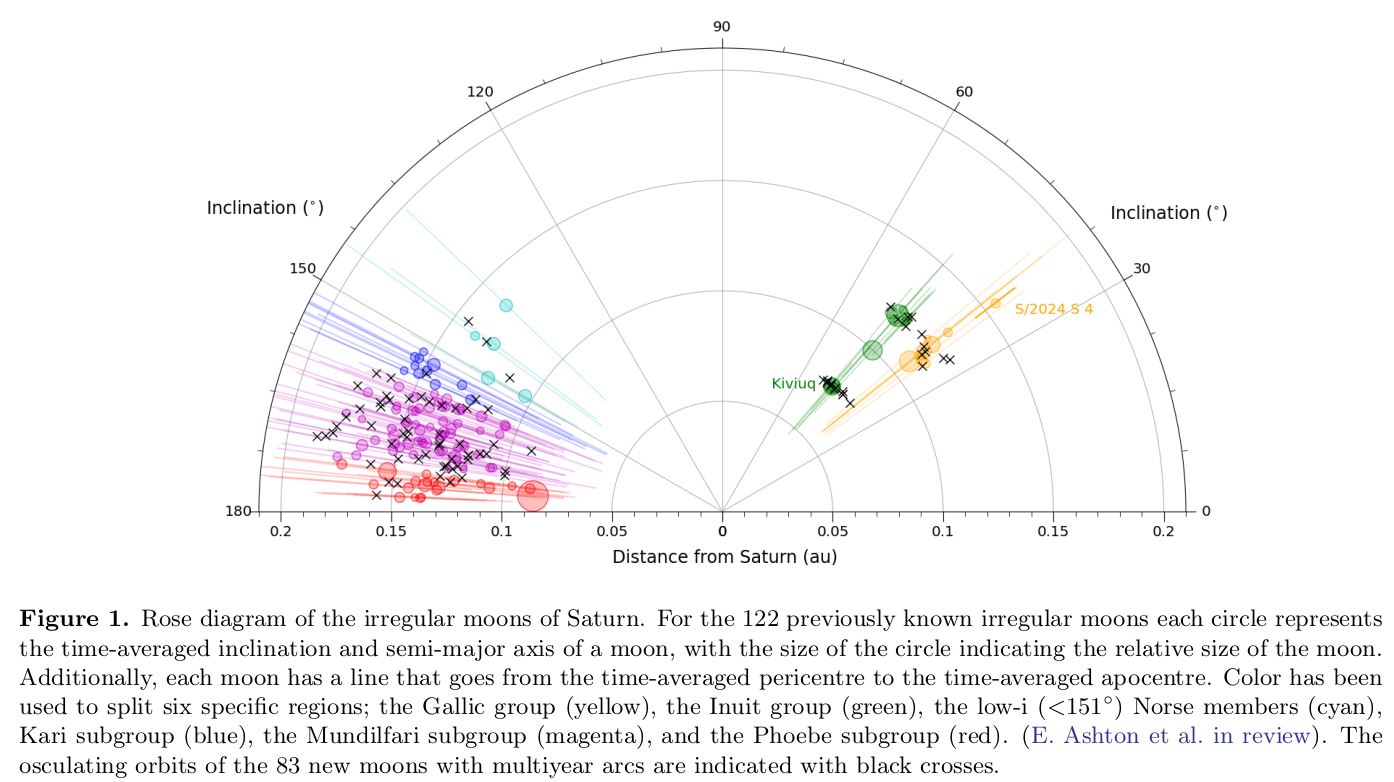
All of the 128 new moons are “irregular moons”, objects captured by their host planet early on in the history of the solar system. “These moons are a few kilometers in size and are likely all fragments of a smaller number of originally captured moons that were broken apart by violent collisions, either with other Saturnian moons or with passing comets,” said Dr. Brett Gladman, professor in the UBC department of Physics and Astronomy (PHAS).
A mystery within Saturn’s irregular moon system was a key motivator for the latest search: given the high number of small compared to large moons, there was likely a collision somewhere within the Saturn system within the last 100 million years – relatively recent in astronomical terms. Otherwise, says Dr. Gladman, any longer and these moons would have collided with each other and been blown into smithereens, which would preferentially reduce the ratio of small moons to bigger ones. Indeed, most of the newly discovered moons are near the Mundilfari subgroup of Saturn’s moons which, given their size, number, and orbital concentration, is the likely the site of the collision. "These studies reveal that the giant planets captured some moderate-sized moons more than 4 billion years ago as the giant planets formed, and we are now seeing moons which are mostly the fragments of those originally-captured moons", said Dr. Gladman.
"Our carefully planned multi-year campaign has yielded a bonanza of new moons that tell us about the evolution of Saturn's irregular natural satellite population," said Dr. Ashton.
The team also includes Dr. Mike Alexandersen, of the Harvard Smithsonian Centre for Astrophysics and received his PhD at PHAS, as well as Dr. Jean-Marc Petit of the Observatoire de Besancon in France.
As for what’s next for the team, their moon-spotting days may be over, for now. “With current technology I don't think we can do much better than what has already been done for moons around Saturn, Uranus and Neptune,” said Dr. Ashton.
French version of this release: French version: 2025 Discovery of more Saturnian Moons | UBC Physics & Astronomy
Press Contact information:
Edward Ashton, Taipei, Taiwan, eashton@asiaa.sinica.edu.tw
Brett Gladman, UBC Vancouver Canada, gladman@astro.ubc.ca
Mike Alexandersen, Cambridge USA, mike.alexandersen@cfa.harvard.edu
Jean-Marc Petit, France, petit@obs-besancon.fr
*Interview language(s): English (Ashton, Gladman, Alexandersen, Petit), French (Gladman, Petit)
Links:
- See UBC Science release here: https://news.ubc.ca/2025/03/saturn-128-new-moons/
- See older 2023 press release here: https://phas.ubc.ca/saturn-re-takes-moon-crown
- Published Summary Discovery in the Research Notes of the AAS
External Links:
- PUBLICATION OF THE MOONS by the International Astronomical Unions Minor Planet Center:
- 61 new saturnian satellites: https://minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K25/K25EF3.html
- 34 new saturnian satellites: https://minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K25/K25EF4.html
- 33 new saturnian satellites: https://minorplanetcenter.net/mpec/K25/K25EF5.html
- Post distribution of this press release, the MPC published the orbits and observations and those observations included linkages back to lost moons observed as long ago as 2004. For 21 of these 33 moons the 2-night of initial observation have resulted in the official discoverer being S. Sheppard et al, now that the abundant new observations have established a high-precision orbit that can be linked back in time.
- New York Times coverage: https://www.nytimes.com/2025/03/11/science/saturn-new-moons.html
- National Geographic coverage: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/saturn-new-moons-record
- Radio Canada: https://ici.radio-canada.ca/nouvelle/2147284/satellites-lune-planete-saturne-decouverte
- Sky and Telescope magazine: https://skyandtelescope.org/astronomy-news/its-official-saturn-has-128-new-moons/