Over the past week, rumours were circulating about a new vulnerability in SSLv3. No details were widely available until today and now we have POODLE, the 'Padding Oracle On Downgraded Legacy Encryption' attack. The attack, specifically against the SSLv3 protocol, allows an attacker to obtain the plaintext of certain parts of an SSL connection, such as the cookie. Similar to BEAST, but more practical to carry out, POODLE could well signal the end of SSLv3 support.
Exploiting POODLE
There are many, great explanations of exactly what POODLE is and how it can be exploited already out on the web, so I won't try to replicate the details here. There are great write ups from OpenSSL and Adam Langley. The whole issue, however, ultimately hinges on the site supporting SSLv3 and the attacker being able to downgrade the client to use SSLv3. These protocol downgrade attacks are old news and are still surfacing to cause problems. By simulating a failure during the negotiation process, an attacker can force a browser and a server to renegotiate using an older protocol, right back down to SSLv3. As the POODLE vulnerability is actually in the protocol itself, this isn't something that can be patched out like ShellShock and HeartBleed.
How to protect your browser
It is also possible to protect yourself from POODLE by disabling SSLv3 support in your browser. This means that even if the server does offer SSLv3 support, your browser will never use it, even during a protocol downgrade attack.
Firefox
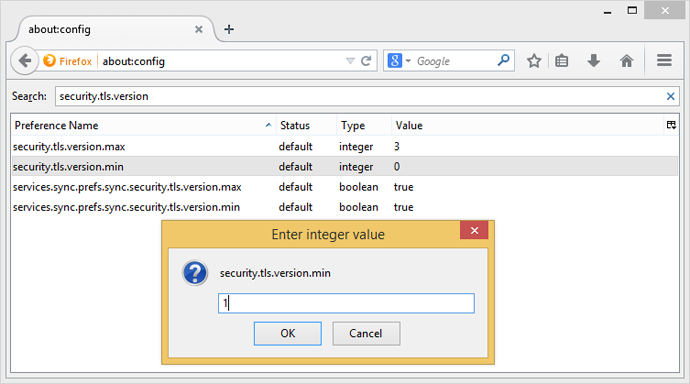
Firefox users can type about:config into their address bar and then security.tls.version.min into the search box. This will bring up the setting that needs to be changed from 0 to 1. The existing setting allows Firefox to use SSLv3 where it's available and if it's required. By changing the setting you will force Firefox to only ever use TLSv1.0 or better, which is not vulnerable to POODLE.
Chrome
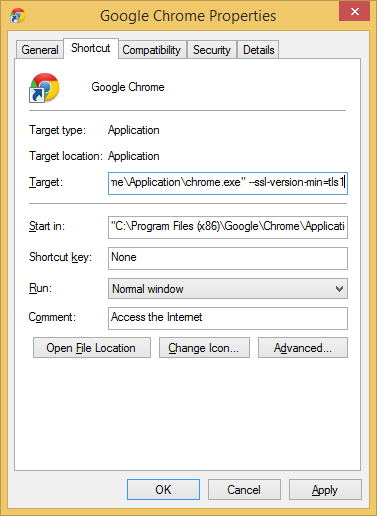
Chrome users don't have an option in the GUI to disable SSLv3 as Google removed it due to confusion over whether SSLv3 or TLSv1 was better with one having a higher numeric value. Instead you can add the command line flag --ssl-version-min=tls1 to enforce the use of TLS and prevent any connection using the SSL protocol. In Windows, right click on your Chrome shortcut, hit Properties and add the command line flag as seen in the image below.
If you use Google Chrome on Mac, Linux, Chrome OS or Android, you can follow these instructions here.
Internet Explorer
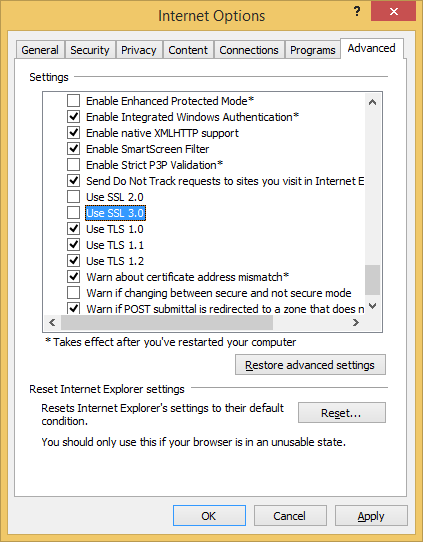
Fixing up Internet Explorer is also pretty easy. Go to Settings, Internet Options and click on the Advanced tab. Scroll down until you see the Use SSL 3.0 checkbox and uncheck it.
How to check your browser
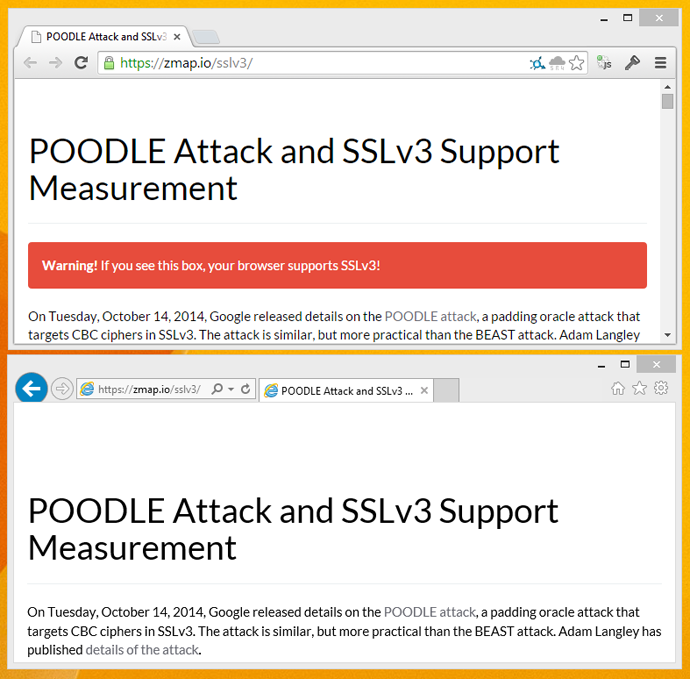
If you want to check that your browser changes have definitely removed SSLv3.0 support there are a couple of sites that you can use. If you visit https://zmap.io/sslv3/ with SSLv3 enabled in your browser, you will see the warning message I'm getting here in Chrome where I haven't yet disabled SSLv3. To double check the site was working as expected, I disabled SSLv3 support in Internet Explorer and opened up the site there too. Here you can see the difference.
There's also the Qualys SSL Client Test to see what your browser supports. Here is my result in Chrome with SSLv3 still enabled:
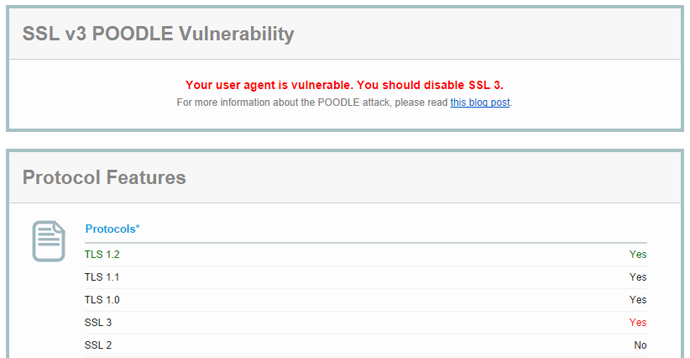
Here is the result in Internet Explorer with SSLv3 disabled:
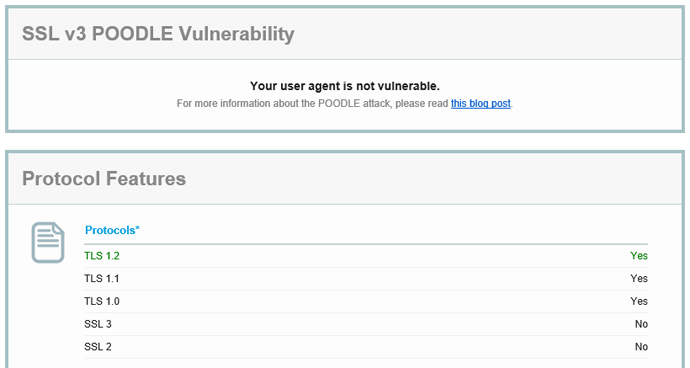
You can also try https://www.poodletest.com/ alongside Zmap and Qualys.
Is there another way?
Google mentioned on their Online Security Blog that they have been using TLS_FALLBACK_SCSV with Chrome and their own servers and mitigated possible protocol downgrade attacks. By introducing a new cipher suite value, TLS_FALLBACK_SCSV {0x56, 0x00}, the browser can indicate to the server that the current connection attempt is a fallback from a previously failed connection attempt and is not using the best protocol it can support. The new cipher suite value is included alongside the existing cipher suite values in the ClientHello message, but as a Signalling Cipher Suite Value (SCSV) it cannot be selected or used by the server as it does not correspond to an actual suite. When the server receives this value, it knows the connection attempt is a fallback and can act upon that information. If the server supports a protocol version higher than the one indicated in the ClientHello when TLS_FALLBACK_SCSV is present, the server must respond with an inappropriate_fallback alert and not proceed with the handshake. The server knows that this connection attempt is not the best protocol the client can support.
Whilst TLS_FALLBACK_SCSV mitigates protocol downgrade attacks, support is not yet widespread, with OpenSSL having only just announced support in version 1.0.1j and Google Chrome being the only browser to currently offer support. Mozilla will disable SSLv3 by default in Firefox 34 which is to be released on Nov 25th and follow up with SCSV support in Firefox 35. All other browsers and web server platforms would need to implement support for this new feature which would then need to be updated to all clients and servers in the wild. Even then, it doesn't actually resolve the POODLE vulnerability, it just means that clients and servers can continue to support SSLv3 where absolutely needed without exposing everyone to the same risk. Ideally, SSLv3 should be consigned to the scrap heap and clients/servers should move on to newer and better protocols like TLS. After all, it is almost 18 years old and was superceeded by TLS 15 years ago...