By week:
|

Week 2 - Rotation-Powered Neutron Stars [1] [3]
Summary
The first neutron stars to be positively identified are the rotation-powered
neutron stars, specifically the radio pulsars. The most famous of the radio
pulsars is the source at the center of the Crab supernova remnant, the Crab
pulsar. The emission from these neutron stars is powered by the rotation
of the neutron star coupled to electromagnetic radiation through the magnetic
dipole moment of the star.
Check out this
Java Applet that simulates the electric field from a moving
charge.
ATNF Pulsar Catalog
and the sounds of pulsars at Princeton Pulsar Group.
Reading List
- ``Rotating Neutron Stars as the Origin of the Pulsating Radio Sources''
[
PDF
]
REF: Gold, T. 1968, Nature, 218, 731 .

- ``Rotating Neutron Stars, Pulsars and Supernova Remnants''
[
PDF
]
REF: Pacini, F. 1968, Nature, 219, 145 .

- ``Pulsar Electrodynamics''
[
ADS,
PDF
]
REF: Goldreich, P., Julian, W. 1969, Astrophys. J., 157, 869
Read Sections I, II, III(a) and IV only.

Problem Set
Problem 1 - Spinning Neutron Stars 
We will estimate how quickly we would expect neutron stars to spin, how
much energy is stored in their spin and other interesting facts about spinning
neutron stars.
-
The sun rotates every 24-30 days depending on latitude. How quickly would it
rotate if it were compressed to 10km in radius while conserving its angular momentum? Its current radius is 7 x 1010 cm.
-
How fast could a neutron star rotate without breaking up? Consider the neutron
star to be 1.4
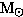 and have a radius of 10 km and compare the
centripetal acceleration of a bit of material on the surface to the
gravitational acceleration. and have a radius of 10 km and compare the
centripetal acceleration of a bit of material on the surface to the
gravitational acceleration.
-
How much angular momentum and rotational energy does a neutron star have? Use
and a spin period of break-up, 1.6 ms, 33 ms and 6 s.
Problem 2 - Original Spin 
If you know the age of a neutron star, its current period and its period
derivative, you can estimate its original spin.
-
Using the results from the lectures, derive a formula for P0 in terms
of the age, current period and period derivative of a pulsar.
-
The table below lists pulsars that are associated with historical supernovae.
Complete the table by calculating the original spin of these neutron stars.
| Name |
Age [yr] |
Period [s] |
P-dot [10-15 s s-1] |
P0 [s] |
| B0531-21 |
949 |
0.0331 |
422.69 |
|
| B0540-69 |
1000 |
0.050 |
480 |
|
| B1951+32 |
64000 |
0.0395 |
5.8 |
|
| J0205+6449 |
822 |
0.06568 |
193 |
|
-
Why do we know the age of the first and last pulsars so accurately?
Last modified: Thursday, 08 April 2010 14:15:29
|