

Next: Raman cooling
Up: Two sub-recoil cooling methods
Previous: Two sub-recoil cooling methods
-Works for He atoms
Level scheme:
Two circularly polarized laser beams resonant on transitions as shown above.
Characterize state of atom by internal quantum numbers and momentum p:
|e0,p> coupled to
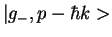 and
and
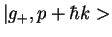 by laser light (closed family of states, neglecting spontaneous emission)
by laser light (closed family of states, neglecting spontaneous emission)
Transition matrix element:
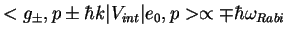 (
(
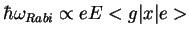 ),
),
sign from Clebsch-Gordan coefficent (given in graph)
Non-absorbing state:

For 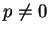 : Mixes with absorbing state
: Mixes with absorbing state
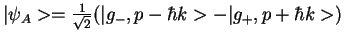
(state vector oscillates between
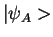 and
and
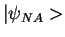 with frequency
with frequency
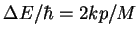 , i.e. the difference in kinetic energy
, i.e. the difference in kinetic energy
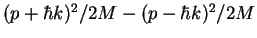 )
)
For p=0 this is a stationary state because
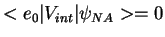 , and also radiatively stable (mixture of ground states)
, and also radiatively stable (mixture of ground states)
Absorption rate of ground state
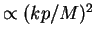 .
.
Atoms with p=0 are trapped in this state indefinitely. Spontaneous emission randomizes p (recoil momentum along z-axis random variable between 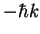 and
and 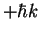 ) and gives atoms chance to fall into the p=0 trap.
) and gives atoms chance to fall into the p=0 trap.
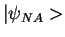 is not a p-eigenstate
is not a p-eigenstate
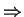 two peaks in momentum distribution
two peaks in momentum distribution

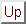

Next: Raman cooling
Up: Two sub-recoil cooling methods
Previous: Two sub-recoil cooling methods
Birger Bergersen
1998-12-12
![\includegraphics[height=12cm,width=10cm,angle=90]{vscpt.ps}](img14.gif)
![\includegraphics[height=12cm,width=10cm,angle=90]{vscpt.ps}](img14.gif)
![\includegraphics[height=12cm,width=10cm,angle=-90]{vscpt2.ps}](img30.gif)